ACC210 Accounting for Decision Making and Control TMA Assignment Question | SUSS
ACC210 Question 1
Cool Strokes Pte Ltd (“CS”) manufactures white board markers for educational use. The company’s markers are sold by the box at $50 each in 20×3. The selling price was increased in 20×4 due to a 50% increase in unit direct material owing to cost pressures. CS used variable costing for internal management reports but its income statement for external reporting is prepared using full absorption costing.
The following data are for the years 20×3 and 20×4:
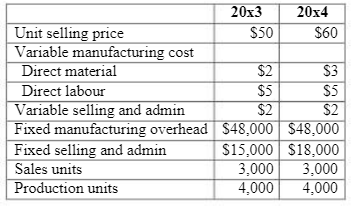
CS uses normal costing and applies manufacturing overheads based on the budgeted production volume for the purpose of absorption costing. CS uses the first-in first-out (FIFO) assumption for the calculation of cost of sales. There was no opening inventory in 20×3. Excess stock from 20×3 is carried forward to 20×4.
Sales in 20×4 remained flat but CS had to incur higher fixed selling and admin costs due to increased marketing efforts to maintain sales. CS rewards production managers if the reported income for the year is maintained or increased over prior year. The CEO was happily ‘surprised’ that profits increased by 25% while maintaining sales volume. He concluded that CS performed better in 20×4 than expected and will recommend a bonus to all staff.
Required:
- Provide a variable costing income statement for each of the two years. Explain why there was a change in profits for 20×4 when compared with the prior year. (18 marks)
- Compare net operating income using absorption costing for the years 20×3 and 20×4. Reconcile the reported income under absorption and variable costing for each of the years using your answer in part (a). Be sure to include explanations relating to cost of goods sold and fixed costs in your reconciliation (in your answer, show unit costs for fixed manufacturing overheads, and fixed selling and admin costs respectively). (26 marks)
- Discuss if CS should continue to use variable costing for internal management instead of full absorption costing? Should the CEO recommend a bonus for all employees for 20×4 performance? Explain
Do You Need Assignment of ACC210 TMA Assignment Question
Order Non Plagiarized Assignment
ACC210 Question 2
Get Fresh Pte Ltd (“GF”) operates a food business in Singapore. Recently, it is considering operating a bubble tea shop under a franchise from Taiwan. It has identified 2 possible locations – one in a shopping mall (Shop A) and the other in a university campus (Shop B). The university is centrally located, and the shop is in an area opened to public. The expected footfall at Shop A is four times that at Shop B. Rent for Shop A is $100,000 per month whereas the rent is $40,000 per month for Shop B. The minimum lease period is 2 years.
Franchisees are required to pay royalties of 6 per cent and a management fee of 5 percent, of sales revenue. They also must purchase several materials and supplies, including tea, pearls, dishwashing liquid and cleaning chemicals from suppliers ‘mandated’ by the franchisor. The prices are generally well above market. These supplies are expected to be 15% of sales revenue on average. The major fixed expense for the franchisee is rental and labour.
The projected costs and revenue for 20×4 are showed below.
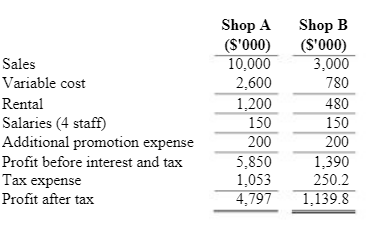
Management fees can be paid annually in a lump sum at the start of each year. Based on the schedule, Shop A is expected to be charged $400,000 and Shop B $120,000 respectively. This arrangement can be changed on a yearly basis. The market for bubble tea is expected to grow by 8% in the next year, 2025 but sales will only expect to maintain at 2025 levels for the next 3 years. For the initial year, the Board has set a target net profit after tax of 50% of sales.
The CEO of GF, Andrew, is confident of the venture but would like more quantitative evidence to support his decision. He has instructed the finance general manager to work out some analysis for the proposal quickly, so he can present to the Board for approval next week.
Required:
(a)For each shop, apply cost-volume-profit analysis to compute the breakeven point (in sales dollars) for the year 20×4 under the following scenarios:
(i)Paying fixed management fee.
(ii)Paying management fee based on percentage of sales revenue
(b) Compute GF’s the degree of operating leverage (nearest 2 dec places) in 20×4 under following scenarios.
(i) Paying fixed management fee.
(11)Paying management fee based on percentage of sales revenue.
(c) If GF selects to operate Shop B under the franchise, which option for management fee should GF choose? What is the margin of safety? Explain.
Compute the estimated sales dollars (rounded to the nearest dollar) which GF needs to achieve for a target profit after tax of $5,000,000 renting Shop A for this venture and paying a variable management fee. Would a fixed management fee be a better option? Explain.
(d) Compute the sales (in nearest dollar) for net income after taxes at which point GF will be indifferent whether it pays a fixed or variable management fee OR rents Shop A or B. Explain what your computations tell you

